Comparative study of pharmacokinetic parameters between clarithromycin and erythromycin stearate in relation to their physicochemical properties.
K Ishii, Y Saito, S Itai, M Nemoto, K Takayama, T Nagai
Index: Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 24(2) , 129-37, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Pharmacokinetic parameters for clarithromycin (CAM) and erythromycin stearate (EMS) were obtained from a model including decomposition in the gastrointestinal tract. To confirm the accuracy of the parameters, various physicochemical properties of both drugs were examined. The ratio of the in vivo dissolution rate, the in vivo decomposition rate and the absorption rate between CAM and EMS were well correlated to the ratio of the in vitro intrinsic dissolution rate, the decomposition rate in the acidic solution, and partition coefficient, respectively. One of the reasons for the excellent absorption of CAM compared with that of EMS was the higher stability in the acidic solution and the higher partition coefficient of CAM. These findings indicate that the ratio of the partition coefficient to the decomposition rate constant in acidic solution plays an important role in determining drug bioavailability for macrolide antibiotics.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
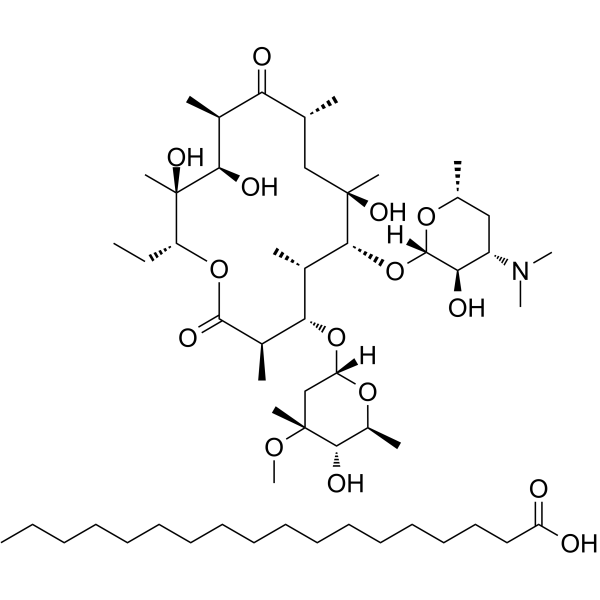 |
Erythromycin stearate
CAS:643-22-1 |
C55H103NO15 |
|
Antibiotics for ureaplasma in the vagina in pregnancy.
2011-01-01 [Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (9) , CD003767, (2011)] |
|
Cholestasis and liver cell damage due to hypersensitivity to...
1999-01-29 [Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 111(2) , 76-7, (1999)] |
|
Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin in comparison with e...
1992-01-01 [Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 24(2) , 219-25, (1992)] |
|
Selective spectrophotometric method for the determination of...
1996-08-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 14(11) , 1625-9, (1996)] |
|
Dental anxiety and the absorption of orally administered ery...
1995-12-01 [Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 80(6) , 660-5, (1995)] |