Probing the penicillin sidechain selectivity of recombinant deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase.
A Dubus, M D Lloyd, H J Lee, C J Schofield, J E Baldwin, J M Frere
Index: Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58(5-6) , 835-43, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Deacetoxycephalosporin C synthase from Streptomyces clavuligerus catalyses the conversion of the five-membered penicillin ring to the unsaturated six-membered cephem ring of deacetoxycephalosporin C. The effects on enzyme activity of the penicillin substrate sidechain and various cofactors were investigated using a continuous spectrophotometric assay. The conversion of penicillin G to phenylacetyl-7-aminodeacetoxycephalo sporanic acid (G-7-ADCA) was confirmed, and further details of the reaction were elucidated. The conversion of ampicillin to cephalexin was faster than that of acetyl-6-APA to acetyl-7-ADCA kcat = 0.120 +/- 0.001 s(-1) versus 0.035 +/- 0.001 s(-1), but they had similar Km values: 4.86 +/- 0.12 and 3.28 +/- 0.26 mM, respectively. Amoxycillin and penicillin V were also converted at low levels. Conversion was not detected for penicillanate, 6-aminopenicillanate, carbenicillin, temocillin, ticarcillin or benzylpenicilloic acid, suggesting that the enzyme has a relatively strict selectivity for the sidechain of the penicillin substrate.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
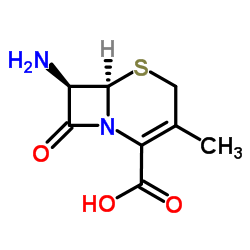 |
7-Aminodeacetoxycephalosporanic acid
CAS:22252-43-3 |
C8H10N2O3S |
|
Enhanced enzymatic synthesis of a semi-synthetic cephalospri...
2003-07-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 25(14) , 1195-8, (2003)] |
|
Enzymatic production of cephalexin.
1994-08-01 [Enzyme Microb. Technol. 16(8) , 715-8, (1994)] |
|
Continuous cultivations of a Penicillium chrysogenum strain ...
2003-08-05 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83(3) , 353-60, (2003)] |
|
Environmentally safe production of 7-aminodeacetoxycephalosp...
2000-08-01 [Nat. Biotechnol. 18(8) , 857-61, (2000)] |
|
Continuous cultivations of a Penicillium chrysogenum strain ...
2003-08-05 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83(3) , 361-8, (2003)] |