Analysis of a substrate specificity switch residue of cephalosporin acylase.
Charles F Sio, Linda G Otten, Robbert H Cool, Wim J Quax
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 312(3) , 755-60, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Residue Phe375 of cephalosporin acylase has been identified as one of the residues that is involved in substrate specificity. A complete mutational analysis was performed by substituting Phe375 with the 19 other amino acids and characterising all purified mutant enzymes. Several mutations cause a substrate specificity shift from the preferred substrate of the enzyme, glutaryl-7-ACA, towards the desired substrate, adipyl-7-ADCA. The catalytic efficiency ( [Formula: see text] (cat)/ [Formula: see text] (m)) of mutant SY-77(F375C) towards adipyl-7-ADCA was increased 6-fold with respect to the wild-type enzyme, due to a strong decrease of [Formula: see text] (m). The [Formula: see text] (cat) of mutant SY-77(F375H) towards adipyl-7-ADCA was increased 2.4-fold. The mutational effects point at two possible mechanisms by which residue 375 accommodates the long side chain of adipyl-7-ADCA, either by a widening of a hydrophobic ring-like structure that positions the aliphatic part of the side chain of the substrate, or by hydrogen bonding to the carboxylate head of the side chain.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
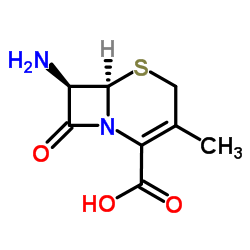 |
7-Aminodeacetoxycephalosporanic acid
CAS:22252-43-3 |
C8H10N2O3S |
|
Enhanced enzymatic synthesis of a semi-synthetic cephalospri...
2003-07-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 25(14) , 1195-8, (2003)] |
|
Enzymatic production of cephalexin.
1994-08-01 [Enzyme Microb. Technol. 16(8) , 715-8, (1994)] |
|
Continuous cultivations of a Penicillium chrysogenum strain ...
2003-08-05 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83(3) , 353-60, (2003)] |
|
Environmentally safe production of 7-aminodeacetoxycephalosp...
2000-08-01 [Nat. Biotechnol. 18(8) , 857-61, (2000)] |
|
Continuous cultivations of a Penicillium chrysogenum strain ...
2003-08-05 [Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83(3) , 361-8, (2003)] |