Sphingomonas sp. strain Lep1: an aerobic degrader of 4-methylquinoline.
S L Pfaller, S D Sutton, B K Kinkle
Index: Can. J. Microbiol. 45(7) , 623-6, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Strain Lep1, isolated from a bacterial consortium capable of aerobic degradation of 4-methylquinoline (4-MQ), was chosen for further characterization as it was the only member of the consortium able to grow on 4-MQ in pure culture. Lep1 was identified as a Sphingomonas sp. based on phylogenetic analysis of 16S rDNA. Furthermore, the presence of sphingolipids and 2-hydroxy fatty acids in the membrane, and a 63% G + C ratio supports the placement of Lep1 in this genus. Additional genetic, physiological, and ecological characterization of bacteria such as Lep1 will allow for the potential exploitation of degradative strains for purposes of bioremediation of contaminated soils.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
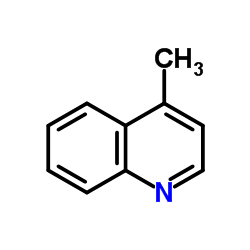 |
lepidine
CAS:491-35-0 |
C10H9N |
|
Time-of-flight accurate mass spectrometry identification of ...
2015-08-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 6159-70, (2015)] |
|
Direct, catalytic, and regioselective synthesis of 2-alkyl-,...
2014-02-07 [Org. Lett. 16(3) , 864-7, (2014)] |
|
A Programmed DNA Marker Based on Bis(4-ethynyl-1,8-naphthali...
2015-11-09 [Chemistry 21 , 16623-30, (2015)] |
|
Microbial metabolism of quinoline and related compounds. XIX...
1993-07-01 [Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 374 , 479-488, (1993)] |
|
Carcinogenicity of quinoline, 4- and 8-methylquinoline and b...
1988-07-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 26(7) , 625-9, (1988)] |