Sen-Sung Cheng, Ju-Yun Liu, Ed-Haun Chang, Shang-Tzen Chang
Index: Bioresour. Technol. 99(11) , 5145-9, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
In this study, the antifungal activities of cinnamaldehyde and eugenol congeners against white-rot fungus Lenzites betulina and brown-rot fungus Laetiporus sulphureus were evaluated and the relationships between the antifungal activity and the chemical structures were also examined. Results from antifungal tests revealed that cinnamaldehyde, alpha-methyl cinnamaldehyde, (E)-2-methylcinnamic acid, eugenol and isoeugenol exhibited strong antifungal activity against all fungi tested. Results derived from the chemical structure-antifungal activity relationship study suggested that compounds with an aldehyde group or an acid group, a conjugated double bond and a length of CH chain outside the ring affect their antifungal properties. Furthermore, the presence of the methyl moiety in the ortho position may have a considerable influence on the inhibitory action against L. betulina and L. sulphureus. In addition, the lipophilicity may play, in part, a crucial role in determining the toxicity of phenylpropenes.
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
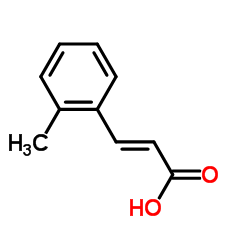 |
715567
CAS:2373-76-4 |
C10H10O2 |
|
Walphos versus Biferrocene-Based Walphos Analogues in the As...
2014-05-01 [Organometallics 33(8) , 1945-1952, (2014)] |
|
Bis-(2,5-diphenylphospholanes) with sp2 carbon linkers: synt...
2008-02-01 [J. Org. Chem. 73(3) , 775-84, (2008)] |
|
Total synthesis and biological evaluation of 22-hydroxyacumi...
2006-02-23 [J. Med. Chem. 49(4) , 1408-12, (2006)] |
Home | MSDS/SDS Database Search | Journals | Product Classification | Biologically Active Compounds | Selling Leads | About Us | Disclaimer
Copyright © 2026 ChemSrc All Rights Reserved