Reaction mechanism for mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase using natural lipoyl domain substrates.
S Liu, X Gong, X Yan, T Peng, J C Baker, L Li, P M Robben, S Ravindran, L A Andersson, A B Cole, T E Roche
Index: Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 386(2) , 123-35, (2001)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) catalyzes a two-step reaction. Recombinant production of substrate amounts of the lipoyl domains of the dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2) component of the mammalian PDC allowed kinetic characterization of the rapid physiological reaction catalyzed by E1. Using either the N-terminal (L1) or the internal (L2) lipoyl domain of E2 as a substrate, analyses of steady state kinetic data support a ping pong mechanism. Using standard E1 preparations, Michaelis constants (Km) were 52 +/- 14 microM for L1 and 24.8 +/- 3.8 microM for pyruvate and k(cat) was 26.3 s(-1). With less common, higher activity preparations of E1, the Km values were > or =160 microM for L1 and > or =35 microM for pyruvate and k(cat) was > or =70 s(-1). Similar results were found with the L2 domain. The best synthetic lipoylated-peptide (L2 residues 163-177) was a much poorer substrate (Km > or =15 mM, k(cat) approximately equals 5 s(-1); k(cat)/Km decreased >1,500-fold) than L1 or L2, but a far better substrate in the E1 reaction than free lipoamide (k(cat)/Km increased >500-fold). Each lipoate source was an effective substrate in the dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) reaction, but E3 had a lower Km for the L2 domain than for lipoamide or the lipoylated peptides. In contrast to measurements with slow E1 model reactions that use artificial acceptors, we confirmed that the natural E1 reaction, using lipoyl domain acceptors, was completely inhibited (>99%) by phosphorylation of E1 and the phosphorylation strongly inhibited the reverse of the second step catalyzed by E1. The mechanisms by which phosphorylation interferes with E1 activity is interpreted based on accrued results and the location of phosphorylation sites mapped onto the 3-D structure of related alpha-keto acid dehydrogenases.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
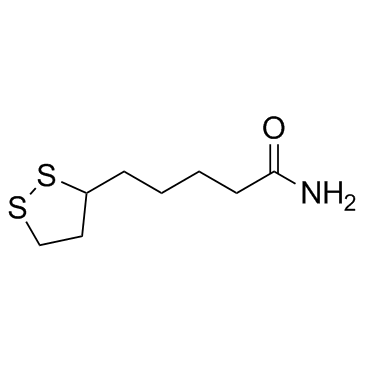 |
Lipoamide
CAS:940-69-2 |
C8H15NOS2 |
|
Sirtuin 4 is a lipoamidase regulating pyruvate dehydrogenase...
2014-12-18 [Cell 159(7) , 1615-25, (2014)] |
|
Molecular characterization of the thioredoxin system from Me...
2014-10-01 [FEBS J. 281(20) , 4598-611, (2014)] |
|
Catalysis of diaphorase reactions by Mycobacterium tuberculo...
2003-02-25 [Biochemistry 42(7) , 2218-28, (2003)] |
|
Efficient reduction of lipoamide and lipoic acid by mammalia...
1996-08-05 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 225(1) , 268-74, (1996)] |
|
Ligand-induced conformational changes and a reaction interme...
2004-04-02 [J. Mol. Biol. 337(4) , 1011-33, (2004)] |