Down-regulation by butylated hydroxytoluene of the number and function of gap junctions in epithelial cell lines derived from mouse lung and rat liver.
X Guan, J Hardenbrook, M J Fernstrom, R Chaudhuri, A M Malkinson, R J Ruch
Index: Carcinogenesis 16(10) , 2575-82, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The mouse pneumotoxicant and lung and liver tumor promoter butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) was examined for its effects on gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) in mouse lung epithelial (C10) and rat liver epithelial (WB-F344) cell lines. GJIC, as measured by fluorescent dye microinjection, was inhibited in both types of cells by BHT in dose- and time-dependent fashions. Inhibition was detected in WB-F344 cells at BHT concentrations > or = 62.5 microM and in C10 cells at concentrations > or = 150 microM after 4 h treatment. Inhibition occurred within 15-30 min and was reversed by removing BHT from the culture medium. The highly toxic BHT metabolite 6-t-butyl-2-(hydroxy-t-butyl)-4-methylphenol (BHTOH) and the non-toxic BHT metabolite, 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxymethylphenol (BHTBzOH) were also tested. In both cell lines BHTOH was a more potent inhibitor of GJIC than BHT, whereas BHTBzOH was ineffective. The mechanisms of inhibition of GJIC by BHT were also examined. The initial rapid inhibition detected within 15-30 min may have been due to gap junction channel closure or blockage, since no changes in gap junction number, connexin (Cx) 43 levels or Cx43 phosphorylation were observed. By 2-4 h, however, gap junctions were internalized into the cytoplasm, the number of immunodetectable plasma membrane gap junctions was reduced and phosphorylated Cx43-P2 was decreased. Treatment of the cells for 24 h with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) prevented inhibition of GJIC by TPA, but not by BHT. Western blot analyses of TPA-treated WB-F344 or C10 cells revealed the presence of a hyperphosphorylated form of Cx43 (Cx43-P3) and no reduction in Cx43-P2, in contrast to BHT-treated cells. These data suggest that BHT and TPA inhibit lung and liver epithelial cell GJIC through distinct mechanisms.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
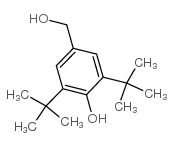 |
3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol
CAS:88-26-6 |
C15H24O2 |
|
Ageing of Neurospora crassa. III. Induction of cellular deat...
1976-01-01 [Mech. Ageing Dev. 5(3) , 163-9, (1976)] |
|
The role of low levels of water in the electrochemical oxida...
2011-07-28 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(28) , 12745-54, (2011)] |
|
Butylated hydroxyanisole specifically inhibits tumor necrosi...
1992-07-01 [Cytokine 4(4) , 269-80, (1992)] |
|
The efficiency of antioxidants delivered by liposomal transf...
1997-08-14 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1328(1) , 1-12, (1997)] |
|
The antioxidant activity of 3, 5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenz...
[J. Am. Chem. Soc. 39(3) , 150-55, (1962)] |