Novel positron emission tomography tracer distinguishes normal from cancerous cells.
Muhammad Saeed, David Sheff, Amnon Kohen
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 286(39) , 33872-8, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Development of tumor-specific probes for imaging by positron emission tomography has broad implications in clinical oncology, such as diagnosis, staging, and monitoring therapeutic responses in patients, as well as in biomedical research. Thymidylate synthase (TSase)-based de novo biosynthesis of DNA is an important target for drug development. Increased DNA replication in proliferating cancerous cells requires TSase activity, which catalyzes the reductive methylation of dUMP to dTMP using (R)-N(5),N(10)-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate (MTHF) as a cofactor. In principle, radiolabeled MTHF can be used as a substrate for this reaction to identify rapidly dividing cells. In this proof-of-principle study, actively growing (log phase) breast cancer (MCF7, MDA-MB-231, and hTERT-HME1), normal breast (human mammary epithelial and MCF10A), colon cancer (HT-29), and normal colon (FHC) cells were incubated with [(14)C]MTHF in culture medium from 30 min to 2 h, and uptake of radiotracer was measured. Cancerous cell lines incorporated significantly more radioactivity than their normal counterparts. The uptake of radioactively labeled MTHF depended upon a combination of cell doubling time, folate receptor status, S phase percentage, and TSase expression in the cells. These findings suggest that the recently synthesized [(11)C]MTHF may serve as a new positron emission tomography tracer for cancer imaging.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
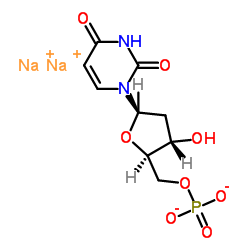 |
Disodium 2'-deoxy-5'-O-phosphonatouridine
CAS:42155-08-8 |
C9H11N2Na2O8P |
|
Simultaneous quantification of 5-FU, 5-FUrd, 5-FdUrd, 5-FdUM...
2009-01-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 877 , 2937-2944, (2009)] |
|
Ultrafast real-time visualization of active site flexibility...
2013-05-28 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(22) , 8924-9, (2013)] |
|
Folate deficiency induces neurodegeneration and brain dysfun...
2008-07-09 [J. Neurosci. 28 , 7219-7230, (2008)] |
|
Crystal structure and enzymatic characterization of thymidyl...
2011-08-01 [Protein Sci. 20(8) , 1398-410, (2011)] |
|
QM/MM study of thymidylate synthase: enzymatic motions and t...
2009-03-12 [J. Phys. Chem. A 113(10) , 2176-82, (2009)] |