Identification of UGT2B9*2 and UGT2B33 isolated from female rhesus monkey liver.
Brian Dean, Byron Arison, Steve Chang, Paul E Thomas, Christopher King
Index: Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 426(1) , 55-62, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Two UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT2B9(*)2 and UGT2B33) have been isolated from female rhesus monkey liver. Microsomal preparations of the cell lines expressing the UGTs catalyzed the glucuronidation of the general substrate 7-hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin in addition to selected estrogens (beta-estradiol and estriol) and opioids (morphine, naloxone, and naltrexone). UGT2B9(*)2 displayed highest efficiency for beta-estradiol-17-glucuronide production and did not catalyze the glucuronidation of naltrexone. UGT2B33 displayed highest efficiency for estriol and did not catalyze the glucuronidation of beta-estradiol. UGT2B9(*)2 was found also to catalyze the glucuronidation of 4-hydroxyestrone, 16-epiestriol, and hyodeoxycholic acid, while UGT2B33 was capable of conjugating 4-hydroxyestrone, androsterone, diclofenac, and hyodeoxycholic acid. Three glucocorticoids (cortisone, cortisol, and corticosterone) were not substrates for glucuronidation by liver or kidney microsomes or any expressed UGTs. Our current data suggest the use of beta-estradiol-3-glucuronidation, beta-estradiol-17-glucuronidation, and estriol-17-glucuronidation to assay UGT1A01, UGT2B9(*)2, and UGT2B33 activity in rhesus liver microsomes, respectively.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
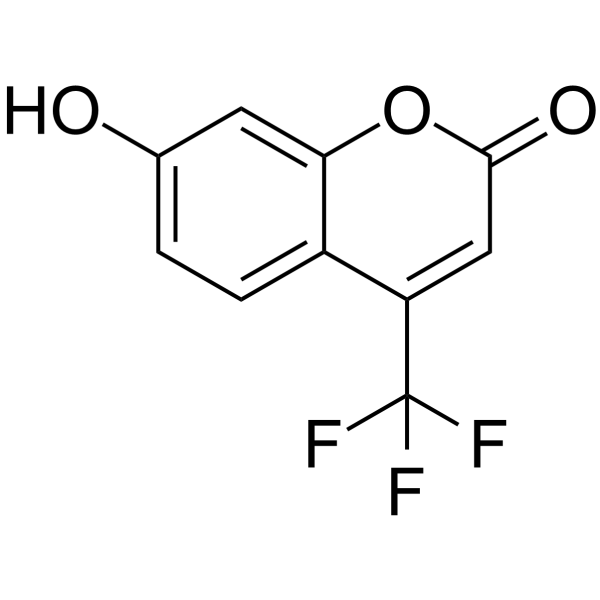 |
7-Hydroxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)coumarin
CAS:575-03-1 |
C10H5F3O3 |
|
HepG2 cells as an in vitro model for evaluation of cytochrom...
2015-01-01 [Arch. Pharm. Res. 38 , 691-704, (2015)] |
|
BFCOD activity in fish cell lines and zebrafish embryos and ...
2015-11-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22 , 16393-404, (2015)] |
|
Environmentally persistent free radical-containing particula...
2015-12-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 289 , 223-30, (2015)] |
|
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 2B4 by environmentally persist...
2015-05-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 95 , 126-32, (2015)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of AMG 232, a novel orally b...
2015-01-01 [Xenobiotica 45 , 681-92, (2015)] |