Effect of Chinese and western antimicrobial agents on selected oral bacteria.
T F Tsao, M G Newman, Y Y Kwok, A K Horikoshi
Index: J. Dent. Res. 61(9) , 1103-6, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The susceptibility of selected oral bacteria, including suspected periodontopathogens, to a commonly employed Chinese herbal medicine Huang-chin (HC, Scutellaria baicalensis) was tested in vitro. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC) were determined. HC was also compared with tetracycline, alexidine, and stannous fluoride. HC decoction, at a concentration of 2%, was bacteriostatic in eight of 11 bacteria tested, but a concentration of 3.13% or greater was required for bactericidal effect. Among the tested bacteria, Bacteroides melaninogenicus ss intermedius was the most sensitive (MIC = 1.57%, MBC = 2%); Actinomyces viscosus was the least sensitive (MIC = 6.25%, MBC = 12.5%). Tetracycline, alexidine, and SnF2 were bactericidal in vitro in all bacteria tested at concentrations lower than those used clinically.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
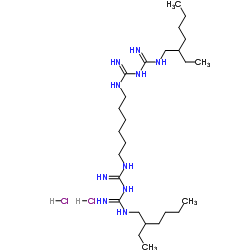 |
Alexidine dihydrochloride
CAS:1715-30-6 |
C26H58Cl2N10 |
|
Chemical interaction of alexidine and sodium hypochlorite.
2012-01-01 [J. Endod. 38(1) , 112-6, (2012)] |
|
Quantitative high throughput screening using a primary human...
2015-01-01 [Nat. Commun. 6 , 6220, (2015)] |
|
Pan-antimicrobial failure of alexidine as a contact lens dis...
2012-07-01 [Eye Contact Lens 38(4) , 222-6, (2012)] |
|
Amoebicidal activities of alexidine against 3 pathogenic str...
2009-01-01 [Eye Contact Lens 35(1) , 1-5, (2009)] |
|
Mechanism of drug failure in fusarium keratitis, 2004-2006.
2014-01-02 [N. Engl. J. Med. 370(1) , 88-9, (2014)] |