| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
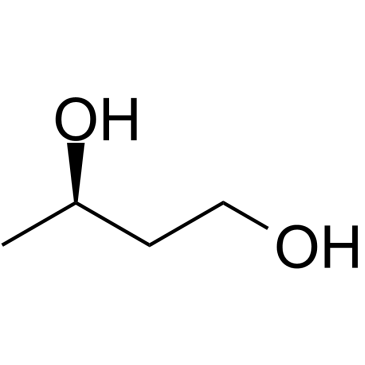 |
(R)-(-)-1,3-Butanediol
CAS:6290-03-5 |
|
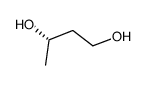 |
(S)-(+)-1,3-BUTANEDIOL
CAS:24621-61-2 |
|
 |
1,3-Butanediol
CAS:107-88-0 |