Accurate measurement of free carnitine in dried blood spots by isotope-dilution electrospray tandem mass spectrometry without butylation.
Andreas Schulze, Christiane Schmidt, Dirk Kohlmüller, Georg F Hoffmann, Ertan Mayatepek
Index: Clin. Chim. Acta 335 , 137-45, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To test the feasibility of free carnitine (FC) determination in dried blood spot specimens (DBS) by stable isotope-dilution electrospray-ionisation tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS).The MS/MS method established for newborn screening, measuring acylcarnitines by positive precursor ion scan of m/z 85 in DBS, was adapted by omitting the butylation and heating step during sample preparation. FC measurement in DBS by this non-butylating MS/MS assay was compared with the butylating MS/MS method and the spectrophotometric Cobas method.FC measurement by the non-butylating MS/MS method meets the demands for a bioanalytical microassay with respect to linearity, detection limit (LOD), accuracy, and precision. Formation of FC was 0-1% and 1-4% in liquid samples and in DBS by the non-butylating MS/MS method, while 3-10% and 8-16% by the butylating method, respectively. Acid-catalysed hydrolysis (butanolysis) in liquid samples was higher for short-chain acylcarnitines (acetyl- and propionylcarnitine). Hydrolysis in DBS was more pronounced for long-chain acylcarnitines. FC concentrations in healthy newborns without butylation were 35% lower than those measured by the established newborn screening assay.The non-butylating MS/MS assay provides a simple and accurate method for FC determination in DBS and represents a trivial but important adaptation of a method already used in many laboratories.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
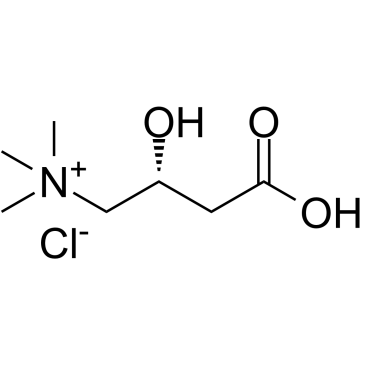 |
L-Carnitine hydrochloride
CAS:6645-46-1 |
C7H16ClNO3 |
|
Amelioration of palmitate-induced metabolic dysfunction in L...
2015-11-01 [Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 93 , 913-22, (2015)] |
|
To Break or to Brake Neuronal Network Accelerated by Ammoniu...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0134145, (2015)] |
|
Regulation of cardiac gene expression by KLF15, a repressor ...
2010-08-27 [J. Biol. Chem. 285 , 27449-27456, (2010)] |
|
Newborn screening for MCAD deficiency: experience of the fir...
2008-01-01 [Can. J. Public Health 99 , 276-80, (2008)] |
|
Effect of pO2 on antitumor drug cytotoxicity on MDR and non-...
2008-01-01 [Anticancer Res. 28 , 55-68, (2008)] |