Farnesylacetone, a sesquiterpenic hormone of Crustacea, inhibits electron transport in isolated rat liver mitochondria.
J Dupont, J F Rodes, J Berreur-Bonnenfant, M C Carre, A Tekitek, P Berreur
Index: Biol. Cell 67(2) , 141-6, (1989)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Farnesylacetone (C18 H30 0) is a male hormone extracted from the androgenic gland of crab, Carcinus maenas. Appropriate enzymatic assays, as well as spectrophotometric studies, indicate that micromolar concentrations of farnesylacetone interact with the electron transport pathway of rat liver mitochondria. By the use of artificial electron donors and electron acceptors, it is shown that farnesylacetone immediately inhibits the electron transfer within complex I (NADH ubiquinone reductase activity) and complex II (succinate ubiquinone reductase activity). It is proposed that farneylacetone could interact with these two complexes of the respiratory chain at the level of the iron-sulfur centers implicated in the dehydrogenase activities. These observations are compared with the results obtained with terpenic molecules which interact with mitochondrial respiration.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
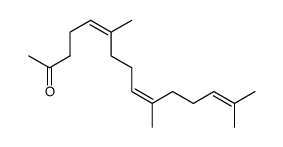 |
Farnesylacetone
CAS:762-29-8 |
C18H30O |
|
Chemical composition of the leaf oil of Actephila excelsa fr...
2014-09-01 [Nat. Prod. Commun. 9(9) , 1359-60, (2014)] |
|
Isolation and characterization of a monoamine oxidase B sele...
2006-05-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14(10) , 3392-8, (2006)] |
|
5E- and 5Z-farnesylacetones from Sargassum siliquastrum as n...
2013-04-01 [Vascul. Pharmacol. 58(4) , 299-306, (2013)] |
|
Modulation of membrane fluidity and lipidic metabolism in tr...
1995-03-01 [Cytometry 19(3) , 217-25, (1995)] |
|
Inhibition of transmethylases by unsaturated carbonyl deriva...
1980-12-01 [Naturwissenschaften 67(12) , 607-8, (1980)] |