Identification of H₂O₂ as a major antimicrobial component in coffee.
Ulla Mueller, Tanja Sauer, Ingrid Weigel, Rohtraud Pichner, Monika Pischetsrieder
Index: Food Funct. 2(5) , 265-72, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Coffee shows distinct antimicrobial activity against several bacterial genera. The present study investigated molecular mechanisms and active ingredients mediating the antimicrobial effect of coffee. Depending on concentration, roasted, but not raw coffee brew inhibited the growth of Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua. Several coffee ingredients with known antibacterial properties were tested for their contribution to the observed effect. In natural concentration, caffeine, ferulic acid and a mixture of all test compounds showed very weak, but significant activity, whereas trigonelline, 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural, chlorogenic acid, nicotinic acid, caffeic acid, and methylglyoxal were not active. Antimicrobial activity, however, was completely abolished by addition of catalase indicating that H(2)O(2) is a major antimicrobial coffee component. In accordance with this assumption, bacterial counts during 16 h of incubation were inversely related to the H(2)O(2) concentration in the incubation solution. Pure H(2)O(2) showed slightly weaker activity. The H(2)O(2) dependent antimicrobial activity of coffee could be mimicked by a reaction mixture of d-ribose and l-lysine (30 min 120 °C) indicating that H(2)O(2) is generated in the coffee brew by Maillard reaction products. Identification of H(2)O(2) as major antimicrobial coffee component is important to evaluate the application of coffee or coffee extracts as natural preservatives.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
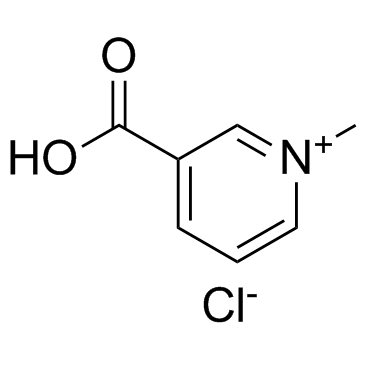 |
Trigonelline chloride
CAS:6138-41-6 |
C7H8ClNO2 |
|
Preliminary studies on trigonelline as potential anti-Alzhei...
2014-10-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 968 , 101-4, (2014)] |
|
Conversion of nicotinic acid to trigonelline is catalyzed by...
2014-10-01 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 452(4) , 1060-6, (2014)] |
|
Pyridine metabolism in tea plants: salvage, conjugate format...
2012-11-01 [J. Plant Res. 125(6) , 781-91, (2012)] |
|
Structure and in vitro antiparasitic activity of constituent...
2011-10-28 [J. Nat. Prod. 74 , 2286-9, (2011)] |
|
Organic and conventional Coffea arabica L.: a comparative st...
2011-06-01 [Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 66(2) , 114-21, (2011)] |