Disorder and twinning in molecular crystals: impurity-induced effects in adipic acid.
L Williams-Seton, R J Davey, H F Lieberman, R G Pritchard
Index: J. Pharm. Sci. 89(3) , 346-54, (2000)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The variation in physical properties of crystals grown in the presence of additives or impurities have previously been attributed to lattice disorder developed during crystallization. Adipic acid crystallized in the presence of a variety of stereochemically related impurities typifies such behavior with disorder manifest in variations of dissolution rates and enthalpies of solution and fusion. In this case the most extreme habit, produced by the presence of added monoalkanoic acids, is a rounded dumbbell that was suggested previously to be a twinned crystal. In this contribution such crystals are fully characterized both through their external morphology and by means of single crystal X-ray diffraction. These techniques show that these particles are not twinned but rather are disordered single crystals comprising a small number of slightly misaligned domains. The interaction between additive and substrate is modeled and new additives selected that induce the formation of true mechanical twins in adipic acid.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
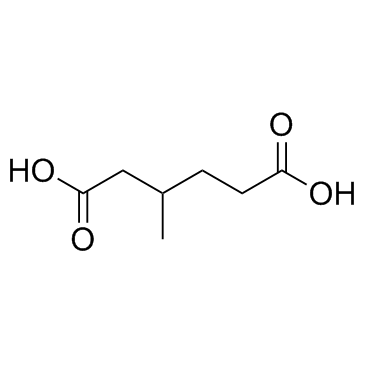 |
3-Methyladipic acid
CAS:3058-01-3 |
C7H12O4 |
|
2,6-Dimethyloctanedioic acid--a metabolite of phytanic acid ...
1983-03-01 [Clin. Chem. 29(3) , 434-7, (1983)] |
|
Metabolism of phytanic acid and 3-methyl-adipic acid excreti...
2003-08-01 [J. Lipid Res. 44(8) , 1481-8, (2003)] |
|
Supramolecular helical mesomorphic polymers. Chiral inductio...
2005-01-12 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(1) , 458-64, (2005)] |
|
Organic acids or urine in multiple sclerosis.
1983-10-01 [Acta Neurol. Scand 68(4) , 231-40, (1983)] |
|
Metabolism of phytanic acid in Refsum's disease.
1982-01-23 [Lancet 1(8265) , 194-6, (1982)] |