Oxidative stress induces myeloperoxidase expression in endocardial endothelial cells from patients with chronic heart failure.
Giampiero La Rocca, Antonino Di Stefano, Ermanno Eleuteri, Rita Anzalone, Francesca Magno, Simona Corrao, Tiziana Loria, Anna Martorana, Claudio Di Gangi, Marilena Colombo, Fabrizio Sansone, Francesco Patanè, Felicia Farina, Mauro Rinaldi, Francesco Cappello, Pantaleo Giannuzzi, Giovanni Zummo
Index: Basic Res. Cardiol. 104(3) , 307-20, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Increased oxidative stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of cardiovascular diseases. Recent findings suggest that myeloperoxidase (MPO) may play a key role in the initiation and maintenance of chronic heart failure (CHF) by contributing to the depletion of the intracellular reservoir of nitric oxide (NO). NO consumption through MPO activity may lead to protein chlorination or nitration, leading to tissue damage. Primary cultures of human endocardial endothelial cells (EEC) obtained at heart transplantation of patients with CHF and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were subjected to oxidative stress by incubation with hydrogen peroxide at non lethal (60 microM) dose for different exposure times (3 and 6 h). Treated and control cells were tested by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR for MPO and 3-chlorotyrosine expression. Both endothelial cell types expressed myeloperoxidase following oxidative stress, with higher levels in EEC. Moreover, 3-chlorotyrosine accumulation in treated cells alone indicated the presence of MPO-derived hypochlorous acid. Immunohistochemistry on sections from post-infarcted heart confirmed in vivo the endothelial positivity to MPO, 3-chlorotyrosine and, to a minor extent, nitrotyrosine. Immunohistochemical observations were confirmed by detection of MPO mRNA in both stimulated EEC and HUVEC cells. This study demonstrates for the first time that EEC can express MPO after oxidative stress, both in vitro and in vivo, followed by accumulation of 3-chlorotyrosine, an end product of oxidative stress. Deregulation of endothelial functions may contribute to the development of a number of cardiovascular diseases, including CHF. The results also highlight the notion that endothelium is not only a target but also a key player in oxidative-driven cardiovascular stress.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
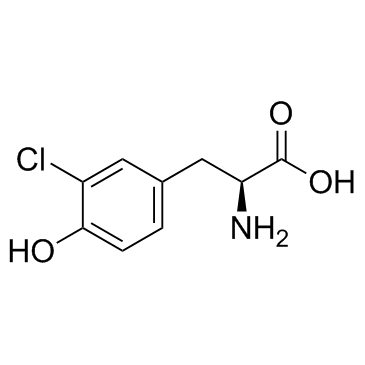 |
3-Chloro-L-tyrosine
CAS:7423-93-0 |
C9H10ClNO3 |
|
Serum and adipose tissue amino acid homeostasis in the metab...
2014-07-03 [J. Proteome Res. 13(7) , 3455-66, (2014)] |
|
Protein stabilization utilizing a redefined codon.
2015-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 5 , 9762, (2015)] |
|
Syntheses of halogen derivatives of L-tryptophan, L-tyrosine...
2016-01-01 [J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 59 , 08-Apr, (2016)] |
|
Plasma concentrations of myeloperoxidase predict mortality a...
2007-05-22 [J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 49(20) , 1993-2000, (2007)] |
|
A high performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical arr...
2010-05-07 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1217 , 3269-3274, (2010)] |