A possible primordial peptide cycle.
Claudia Huber, Wolfgang Eisenreich, Stefan Hecht, Gunter Wächtershäuser
Index: Science 301(5635) , 938-40, (2003)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
alpha-Amino acids can undergo peptide formation by activation with carbon monoxide (CO) under hot aqueous conditions in the presence of freshly coprecipitated colloidal (Fe,Ni)S. We now show that CO-driven peptide formation proceeds concomitantly with CO-driven, N-terminal peptide degradation by racemizing N-terminal hydantoin and urea derivatives to alpha-amino acids. This establishes a peptide cycle with closely related anabolic and catabolic segments. The hydantoin derivative is a purin-related heterocycle. The (Fe,Ni)S-dependent urea hydrolysis could have been the evolutionary precursor of the nickelenzyme urease. The results support the theory of a chemoautotrophic origin of life with a CO-driven, (Fe,Ni)S-dependent primordial metabolism.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
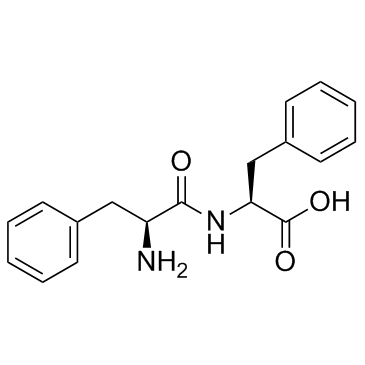 |
H-Phe-Phe-OH
CAS:2577-40-4 |
C18H20N2O3 |
|
Metabolomic profiling of serum in the progression of Alzheim...
2014-12-01 [Electrophoresis 35(23) , 3321-30, (2014)] |
|
Possible mechanism of uptake for several compounds in ionize...
1984-01-30 [Life Sci. 34(5) , 427-36, (1984)] |
|
pH-dependence of complexion constants and complex mobility i...
2001-09-01 [Electrophoresis 22(15) , 3163-70, (2001)] |
|
Enzymatic digestibility of peptides cross-linked by ionizing...
1984-03-01 [Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 45(3) , 283-95, (1984)] |
|
A symmetric inhibitor binds HIV-1 protease asymmetrically.
1993-01-26 [Biochemistry 32(3) , 937-47, (1993)] |