Acrolein genotoxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. III. Effects of metabolism modification.
A R Barros, L M Sierra, M A Comendador
Index: Mutat. Res. 321(3) , 119-26, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In order to investigate the role of metabolism in acrolein genotoxicity in D. melanogaster, the action of several metabolism modifiers, namely phenobarbital, an inducer of xenobiotic metabolism, phenylimidazole and iproniazid, inhibitors of oxidative activities of cytochrome P450, and diethyl maleate, a glutathione-depleting agent, have been assayed using the sex-linked recessive lethal (SLRL) test, with two different administration routes (feeding and injection). The results support the hypothesis that acrolein is not only a direct mutagen but is also transformed, by oxidative activities of cytochrome P450 after glutathione conjugation, into an active metabolite, possibly glycidaldehyde. Moreover, acrolein is deactivated by an enzymatic activity induced by phenobarbital.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
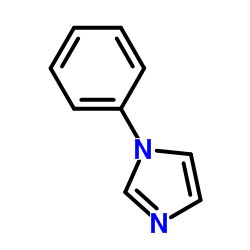 |
1-Phenylimidazole
CAS:7164-98-9 |
C9H8N2 |
|
Influence of inhibition of the metabolic activation on the m...
1988-11-01 [Mutat. Res. 202(1) , 251-67, (1988)] |
|
Calmodulin-dependent nitric-oxide synthase. Mechanism of inh...
1993-05-05 [J. Biol. Chem. 268(13) , 9425-9, (1993)] |
|
Three-dimensional pharmacophore hypotheses for the locust ne...
1999-07-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7(7) , 1437-43, (1999)] |
|
Chloroform-induced cytolethality in freshly isolated male B6...
1998-04-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 149(2) , 217-25, (1998)] |
|
Active-site structure analysis of recombinant human inducibl...
1996-07-23 [Biochemistry 35(29) , 9567-75, (1996)] |