| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
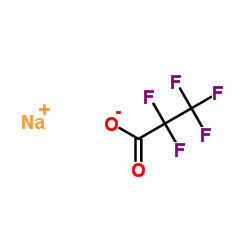 |
Sodium pentafluoropropanoate
CAS:378-77-8 |
|
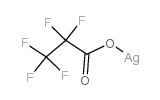 |
Propanoic acid,2,2,3,3,3-pentafluoro-, silver(1+) salt (1:1)
CAS:509-09-1 |
|
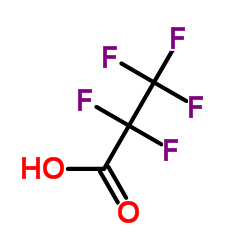 |
Pentafluoropropanoic acid
CAS:422-64-0 |