N-4-iodophenyl-N'-2-chloroethylurea, a novel potential anticancer agent with colon-specific accumulation: radioiodination and comparative in vivo biodistribution profiles.
Emmanuelle Mounetou, Elisabeth Miot-Noirault, René C Gaudreault, J Claude Madelmont
Index: Invest. New Drugs 28(2) , 124-31, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
In a search for more selective anticancer drugs, we have designed nitrogen mustard and nitrosourea conjugates leading to a series of N-4-aryl-N'-2-chloroethylureas (CEUs). The iodinated derivative N-4-iodophenyl-N'-2-chloroethylurea (4-ICEU) has demonstrated significant antineoplastic and antiangiogenic potency in preclinical evaluations. In this study, 4-ICEU was radiolabelled with [(125)I]iodide in order to carry out a comparative study of its in vivo behavior profile. 4-[(125)I]-ICEU was synthesized by direct electrophilic radioiodination with 80% radiochemical yield and 97% radiopurity. Three different routes of administration (intraperitoneal (ip), intravenous (iv) and intratumoral (it)) were tested in mice bearing subcutaneously implanted CT-26 murine colon carcinoma. The results clearly established that 4-ICEU was more stable to biotransformation than previously studied CEUs congeners. It was readily bioavailable and reached the CT-26 colorectal tumor regardless of the route of administration. Additionally, the colon mucosa was an important target tissue where 4-ICEU accumulated and remained largely untransformed. In conclusion, these results justify further investigations for developing 4-ICEU as a new chemotherapeutic agent for colorectal cancer.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
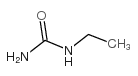 |
Ethylurea
CAS:625-52-5 |
C3H8N2O |
|
Solvation of human serum albumin in aqueous alkylurea soluti...
1993-10-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 42(4) , 320-5, (1993)] |
|
Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by alkylureas.
1991-12-01 [AIDS 5(12) , 1447-52, (1991)] |
|
Neoplasia induced in male rats fed lead acetate, ethyl urea,...
1985-01-01 [Toxicol. Pathol. 13(1) , 50-7, (1985)] |
|
Mutagenic effects of nitrogen dioxide combined with methylur...
1981-03-01 [Mutat. Res. 88(3) , 281-90, (1981)] |
|
Comparison of nicotinamide, ethylurea and polyethylene glyco...
1997-10-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45(10) , 1688-93, (1997)] |