Alterations in the reproductive performance of habrobracon females following combined treatments with ethylurea and sodium nitrate or nitrite.
D S Grosch
Index: Mutat. Res. 88(2) , 179-89, (1981)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Ethylurea (EU) and NaNO2 fed simultaneously to female braconid wasps caused several types of changes in reproductive performance. Early effects included a decrease in (a) the number of vitellogenic oocytes developing into eggs, and in (b) the hatchability of the eggs laid. After a period of no damage to transitional cells there was a late effect expressed as a pronounced reduction in the number of eggs produced from the oogonia, although the hatchability was good. Dissection of the ovarioles revealed gaps in the oogenetic sequence. Most of the specimens showed resorption of the small oocytes and some specimens contained distal masses of undifferentiated cells resembling a tumerous condition. Neither EU nor NaNO2 alone caused the damage obtained from feeding them in combination, and EU injected along with NaNO2 was ineffective.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
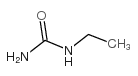 |
Ethylurea
CAS:625-52-5 |
C3H8N2O |
|
Solvation of human serum albumin in aqueous alkylurea soluti...
1993-10-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 42(4) , 320-5, (1993)] |
|
Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by alkylureas.
1991-12-01 [AIDS 5(12) , 1447-52, (1991)] |
|
Neoplasia induced in male rats fed lead acetate, ethyl urea,...
1985-01-01 [Toxicol. Pathol. 13(1) , 50-7, (1985)] |
|
Mutagenic effects of nitrogen dioxide combined with methylur...
1981-03-01 [Mutat. Res. 88(3) , 281-90, (1981)] |
|
Comparison of nicotinamide, ethylurea and polyethylene glyco...
1997-10-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45(10) , 1688-93, (1997)] |