Catalytic addition of alkyne C-H, amine N-H, and phosphine P-H bonds to carbodiimides: an efficient route to propiolamidines, guanidines, and phosphaguanidines.
Wen-Xiong Zhang, Zhaomin Hou
Index: Org. Biomol. Chem. 6(10) , 1720-30, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Various metal complexes (e.g., lanthanides, early transition metals, and alkali metals) can serve as catalyst precursors for the catalytic addition of alkyne C-H, amine N-H, and phosphine P-H bonds to carbodiimides, to give a new family of propiolamidines, guanidines, and phosphaguanidines, some of which were difficult to prepare previously. The catalytic reaction proceeds generally through nucleophilic addition of an M-ER (E=CR(1)R(2), NR(1), PR(1)) bond, which is formed by an acid-base reaction between a catalyst precursor and a RE-H bond, to a carbodiimide compound, followed by protonolysis of the resultant amidinate-(phospha)guanidinate species "{R'NC(ER)NR'}M" with RE-H.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
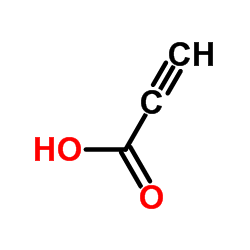 |
Propiolic acidd
CAS:471-25-0 |
C3H2O2 |
|
Identification of the toxic trigger in mushroom poisoning.
2009-07-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 465-7, (2009)] |
|
Hierarchically functionalized magnetic core/multishell parti...
2015-01-01 [ACS Nano 9 , 4219-26, (2015)] |
|
Development of a tailor-made bis(oxazolidine)pyridine-metal ...
2013-09-14 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 49(71) , 7776-8, (2013)] |
|
Copper-catalyzed oxidative decarboxylative couplings of sulf...
2013-12-20 [Org. Lett. 15(24) , 6155-7, (2013)] |
|
Study of 1,4-dihydropyridine structural scaffold: discovery ...
2009-09-10 [J. Med. Chem. 52 , 5496-504, (2009)] |