Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase is essential for activation of TRPC5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells.
Shunichi Shimizu, Takashi Yoshida, Minoru Wakamori, Masakazu Ishii, Takaharu Okada, Masami Takahashi, Minoru Seto, Katsuhiko Sakurada, Yuji Kiuchi, Yasuo Mori
Index: J. Physiol. 570(Pt 2) , 219-35, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Mammalian homologues of Drosophila transient receptor potential (TRP) proteins are responsible for receptor-activated Ca(2+) influx in vertebrate cells. We previously reported the involvement of intracellular Ca(2+) in the receptor-mediated activation of mammalian canonical transient receptor potential 5 (TRPC5) channels. Here we investigated the role of calmodulin, an important sensor of changes in intracellular Ca(2+), and its downstream cascades in the activation of recombinant TRPC5 channels in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells. Ca(2+) entry through TRPC5 channels, induced upon stimulation of the G-protein-coupled ATP receptor, was abolished by treatment with W-13, an inhibitor of calmodulin. ML-9 and wortmannin, inhibitors of Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK), and the expression of a dominant-negative mutant of MLCK inhibited the TRPC5 channel activity, revealing an essential role of MLCK in maintaining TRPC5 channel activity. It is important to note that ML-9 impaired the plasma membrane localization of TRPC5 channels. Furthermore, TRPC5 channel activity measured using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique was inhibited by ML-9, whereas TRPC5 channel activity observed in the cell-excised, inside-out patch was unaffected by ML-9. An antibody that recognizes phosphorylated myosin light chain (MLC) revealed that the basal level of phosphorylated MLC under unstimulated conditions was reduced by ML-9 in HEK293 cells. These findings strongly suggest that intracellular Ca(2+)-calmodulin constitutively activates MLCK, thereby maintaining TRPC5 channel activity through the promotion of plasma membrane TRPC5 channel distribution under the control of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation equilibrium of MLC.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
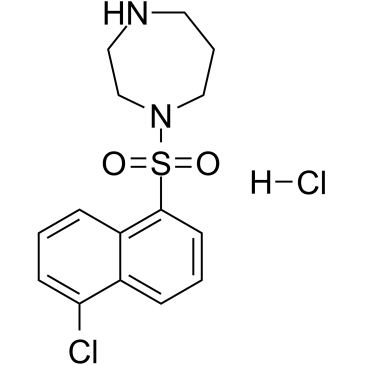 |
ML-9
CAS:105637-50-1 |
C15H18Cl2N2O2S |
|
Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape.
2013-10-22 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(43) , 17253-8, (2013)] |
|
Calcium-Dependent Isoforms of Protein Kinase C Mediate Postt...
2011-06-09 [Neuron 70(5) , 1005-19, (2011)] |
|
Linalyl acetate as a major ingredient of lavender essential ...
2006-07-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 48(1) , 850-6, (2006)] |
|
A force-activated kinase in a catch smooth muscle.
2011-03-01 [J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 31(5-6) , 349-58, (2011)] |
|
Mechanisms of Rho kinase regulation of vascular reactivity f...
2008-01-01 [Shock 29(1) , 65-70, (2008)] |