A force-activated kinase in a catch smooth muscle.
Thomas M Butler, Marion J Siegman
Index: J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 31(5-6) , 349-58, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Permeabilized anterior byssus retractor muscles (ABRM) from Mytilus edulis were used as a simple system to test whether there is a stretch dependent activation of a kinase as has been postulated for titin and the mini-titin twitchin. The ABRM is a smooth muscle that shows catch, a condition of high force maintenance and resistance to stretch following stimulation when the intracellular Ca(++) concentration has diminished to sub-maximum levels. In the catch state twitchin is unphosphorylated, and the muscle maintains force without myosin crossbridge cycling through what is likely a twitchin mediated tether between thick and thin filaments. In catch, a small change in length results in a large change in force. The phosphorylation state of an added peptide, a good substrate for molluscan twitchin kinase, with the sequence KKRAARATSNVFA was used as a measure of kinase activation. We find that there is about a two-fold increase in phosphorylation of the added peptide with a 10% stretch of the ABRM in catch. The increased phosphorylation is due to activation of a kinase rather than to an inhibition of a phosphatase. The extent of phosphorylation of the peptide is decreased when twitchin is phosphorylated and catch force is not present. However, there is also a large increase in peptide phosphorylation when the muscle is activated in pCa 5, and the catch state does not exist. The force-sensitive kinase activity is decreased by ML-9 and ML-7 which are inhibitors of twitchin kinase, but not by the Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632. There is no detectable phosphorylation of myosin light chains, but the phosphorylation of twitchin increases by a small, but significant extent with stretch. It is possible that twitchin senses force output resulting in a force-sensitive twitchin kinase activity that results in autophosphorylation of twitchin on site(s) other than those responsible for relaxation of catch.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
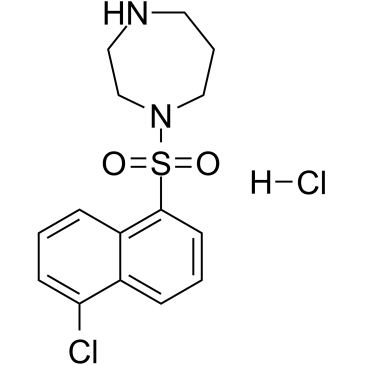 |
ML-9
CAS:105637-50-1 |
C15H18Cl2N2O2S |
|
Modulation of macrophage phenotype by cell shape.
2013-10-22 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(43) , 17253-8, (2013)] |
|
Calcium-Dependent Isoforms of Protein Kinase C Mediate Postt...
2011-06-09 [Neuron 70(5) , 1005-19, (2011)] |
|
Linalyl acetate as a major ingredient of lavender essential ...
2006-07-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 48(1) , 850-6, (2006)] |
|
Mechanisms of Rho kinase regulation of vascular reactivity f...
2008-01-01 [Shock 29(1) , 65-70, (2008)] |
|
Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase is essen...
2006-01-15 [J. Physiol. 570(Pt 2) , 219-35, (2006)] |