| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
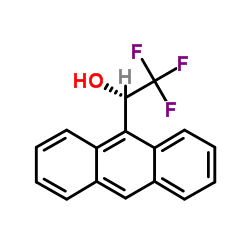 |
(+)-Pirkle's Alcohol
CAS:60646-30-2 |
|
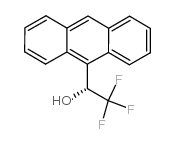 |
(r)-(-)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(9-anthryl)ethanol
CAS:53531-34-3 |