| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-Hydroxyproline
CAS:51-35-4 |
|
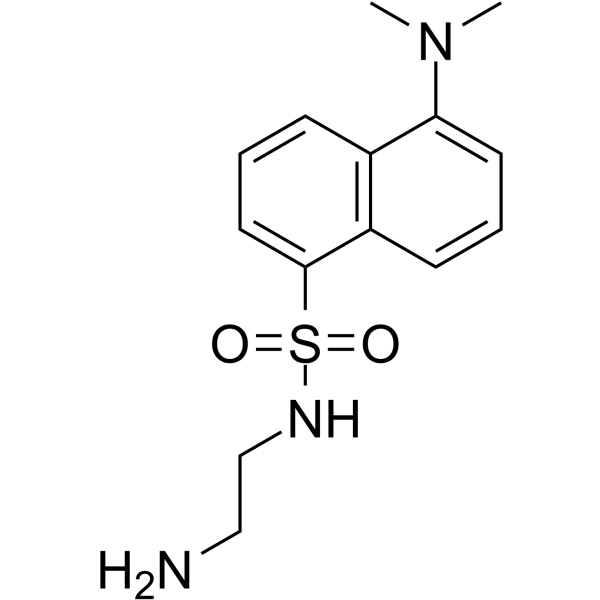 |
Dansyl Ethylenediamine
CAS:35060-08-3 |