| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
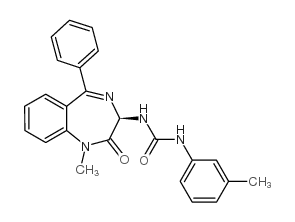 |
L-365,260
CAS:118101-09-0 |
|
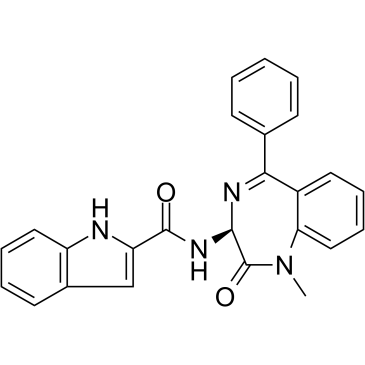 |
Devazepide
CAS:103420-77-5 |