| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
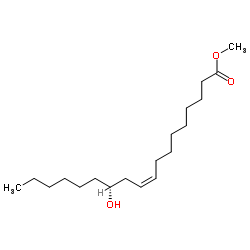 |
RICINOLEIC ACID, METHYL ESTER
CAS:141-24-2 |
|
 |
R-γ-Decalactone
CAS:706-14-9 |