| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
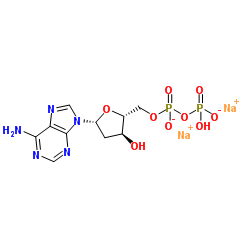 |
2'-Deoxyadenosine-5'-diphosphate disodium salt
CAS:72003-83-9 |
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
2'-Deoxyadenosine-5'-diphosphate disodium salt
CAS:72003-83-9 |