m-Fluorotyrosine substitution in beta-galactosidase; evidence for the existence of a catalytically active tyrosine.
M Ring, I M Armitage, R E Huber
Index: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 131(2) , 675-80, (1985)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The pH profiles of beta-galactosidase, having tyr replaced by m-fluorotyrosine, were compared to those of normal enzyme. The inflection point on the alkaline side was lowered about 1.5 pH units in the fluoro-enzyme, corresponding to the difference in the phenolic pKa values of m-fluorotyrosine and tyr. When glycosidic bond breakage was rate-limiting, the Vm at pH 7.0 was higher for the fluoro-enzyme. When hydrolysis was rate-limiting or when acceptors which made transgalactosylis rate-limiting were used, the Vm was lower for the fluoro-enzyme. This shows that a tyr in beta-galactosidase is a general-acid catalyst in the glycosidic bond breaking reaction and a tyr (probably the same one) is a general-base catalyst in the hydrolytic reaction.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
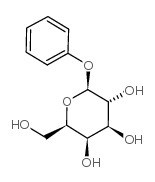 |
Phenylgalactoside
CAS:2818-58-8 |
C12H16O6 |
|
Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects mouse brain against D-g...
2015-06-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 133 , 122-31, (2015)] |
|
Structure-based drug design and optimization of mannoside ba...
2010-06-24 [J. Med. Chem. 53 , 4779-92, (2010)] |
|
Transdifferentiation of mouse adipose-derived stromal cells ...
2015-05-15 [Exp. Cell Res. 334 , 160-72, (2015)] |
|
Drosophila KASH-domain protein Klarsicht regulates microtubu...
2015-11-01 [Dev. Biol. 407 , 103-14, (2015)] |
|
COX-2 suppresses tissue factor expression via endocannabinoi...
2007-09-03 [J. Exp. Med. 204 , 2053-61, (2007)] |