| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
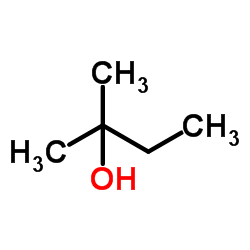 |
tert-Amyl Alcohol
CAS:75-85-4 |
|
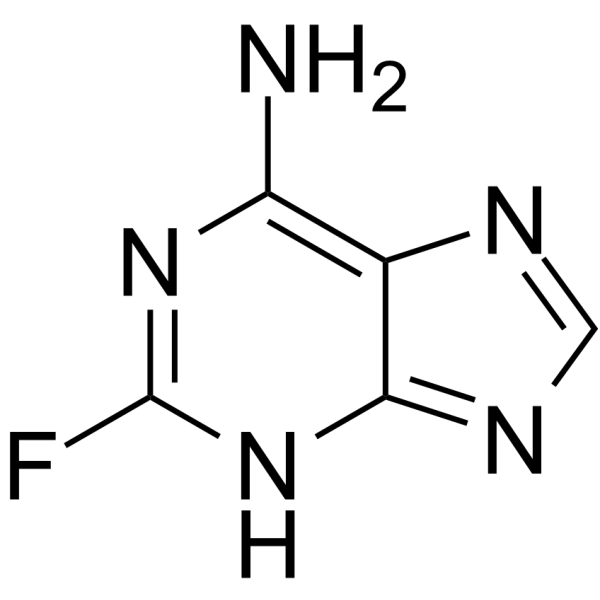 |
TCMDC-124283
CAS:700-49-2 |