Hexofuranosyl thymidines inserted into oligodeoxynucleotides via their two exocyclic hydroxy groups. Oligo synthesis and RNase H activity.
Vyacheslav V Filichev, Birte Vester, Erik B Pedersen
Index: Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12 , 2843-2851, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Hexofuranosyl nucleosides are considered as conformationally restricted acyclic nucleosides using a furanose ring to link the diol backbone to the nucleobase. The phosphoramidite of 1-(2,3-dideoxy-beta-D-erythro-hexofuranosyl)thymine was synthesized from thymidine with formation of a new stereocentre at C-5' and the nucleoside was used in oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) synthesis. Binding of mixed sequence ODNs towards complementary DNA and RNA showed decreased affinity compared to the wild-type oligos. Insertion in the middle of poly alphaT sequence led to stabilization of ODN/dA(14) duplexes at low ionic strength, but a decrease was observed in medium and high salt buffers compared to d(alphaT)(14)/dA(14). Both beta and alpha hexofuranosyl thymidines allowed cleavage of complementary mixed-sequence RNA by RNase H to the 3'-site of the modification in ODNs whereas a limited inhibition was detected from the 5'-site.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
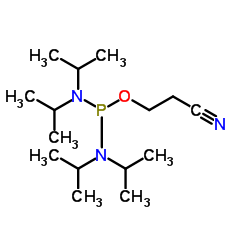 |
2-Cyanoethyltetraisopropylphosphorodiamidite
CAS:102691-36-1 |
C15H32N3OP |
|
2'-fluoro-4'-thioarabino-modified oligonucleotides: conforma...
2007-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 35(5) , 1441-51, (2007)] |
|
DNA adducts of acrolein: site-specific synthesis of an oligo...
2002-05-01 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15(5) , 607-13, (2002)] |
|
Synthesis and fluorescence studies of multiple labeled oligo...
2004-01-01 [Bioconjug. Chem. 15 , 638-646, (2004)] |
|
Application of 2-cyanoethyl N,N,N',N'-tetraisopropylphosphor...
1986-09-25 [Nucleic Acids Res. 14(18) , 7391-403, (1986)] |
|
Synthesis of 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerophosphatidylserine from eg...
1996-05-01 [Lipids 31(5) , 541-6, (1996)] |