A single receptor encoded by vzg-1/lpA1/edg-2 couples to G proteins and mediates multiple cellular responses to lysophosphatidic acid.
N Fukushima, Y Kimura, J Chun
Index: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95 , 6151-6156, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Extracellular lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) produces diverse cellular responses in many cell types. Recent reports of several molecularly distinct G protein-coupled receptors have raised the possibility that the responses to LPA stimulation could be mediated by the combination of several uni-functional receptors. To address this issue, we analyzed one receptor encoded by ventricular zone gene-1 (vzg-1) (also referred to as lpA1/edg-2) by using heterologous expression in a neuronal and nonneuronal cell line. VZG-1 expression was necessary and sufficient in mediating multiple effects of LPA: [3H]-LPA binding, G protein activation, stress fiber formation, neurite retraction, serum response element activation, and increased DNA synthesis. These results demonstrate that a single receptor, encoded by vzg-1, can activate multiple LPA-dependent responses in cells from distinct tissue lineages.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
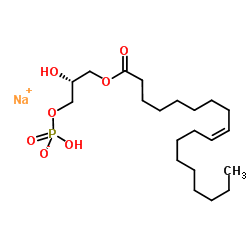 |
1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid sodium salt
CAS:22556-62-3 |
C21H40NaO7P |
|
Somatostatin inhibits cell migration and reduces cell counts...
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6 , e19740, (2011)] |
|
Lysophosphatidic acid alters the expression profiles of angi...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0122060, (2015)] |
|
Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates prostaglandin E2 production...
2009-08-01 [Exp. Biol. Med. 234 , 986-93, (2009)] |
|
γ-Tubulin localizes at actin-based membrane protrusions and ...
2011-01-01 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 408 , 248-52, (2011)] |
|
Lysophosphatidic acid: mitogen and motility factor.
2003-12-01 [Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31 , 1209-1212, (2003)] |