Cytogenetic effects of the herbicide chloridazon in cultured sheep lymphocytes.
K Siviková, J Dianovský
Index: Acta Vet. Hung. 45(1) , 11-6, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effect of in vitro exposure to the herbicide chloridazon on the induction of chromosome aberrations (CA) and sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) was studied in cultured sheep peripheral lymphocytes. A positive clastogenic effect was observed in chloridazon-treated cultures at a dose of 7 x 10(-4) M both in the presence and absence of the S9 fraction, but no significant increase of chromosome breaks was seen at lower doses (7 x 10(-6) M and 7 x 10(-5) M, respectively). A clear dose-dependence and significant differences were found in chloridazon potency to induce SCEs. Induction of cell cycle delays as compared to the controls was not observed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
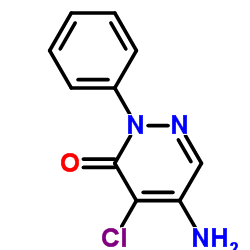 |
Chloridazon
CAS:1698-60-8 |
C10H8ClN3O |
|
Destruction of halogen-containing pesticides by means of det...
2013-02-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(2) , 855-61, (2013)] |
|
Prevention of chloridazon and metribuzin pollution using lig...
2010-01-01 [Environ. Pollut. 158(5) , 1412-9, (2010)] |
|
Time- and dose-dependent induction of HSP70 in Lemna minor e...
2011-09-01 [Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 87(3) , 226-30, (2011)] |
|
Phytotoxicity and antioxidative enzymes of green microalga (...
2012-09-01 [J. Environ. Sci. Health B 47(8) , 814-22, (2012)] |
|
Rapid extraction and capillary gas chromatography for diazin...
1995-04-27 [Forensic Sci. Int. 72(3) , 199-207, (1995)] |