Induction and suppression of murine CYP-mediated biotransformation by dithianon: organ- and sex-related differences.
L Pozzetti, M Paolini, J Barillari, G Cantelli-Forti
Index: Cancer Lett. 141(1-2) , 47-56, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
With the aim of evaluating the co-carcinogenic properties of dithianon, the regio- and stereo-selective hydroxylation of testosterone was used as a multibiomarker of effect for cytochrome P450 (CYP) changes. CYP-catalysed reactions have been studied in liver, kidney and lung microsomes from male and female Swiss albino CD1 mice treated i.p. with single (3 or 6 mg/kg body wt.) or repeated (3 mg/kg body wt. daily for 3 days) doses of this fungicide. Induction or suppression was recorded under various situations in different organs and sexes. In liver, all testosterone hydroxylase (TH) activities were increased in the single treatment from 2.8- (6beta-, 16alpha- and 16beta-TH activities) to 16-fold (2beta-TH activity) in males at the lower dose. In contrast, activities were reduced from 33.3% (16beta- and 17-TH activities, lower dose) to 66.4% (16beta-TH activity, higher dose) in females. In kidney, a similar pattern of modulation was achieved: induction from 2.9- to 5-fold (6beta- and 2alpha-TH activities, higher and lower doses, respectively) in males; suppression from 47.4 to 50.2% (2alpha- and 2beta-TH activities, either at lower or higher doses) in females. In lung, a significant induction ranging from 7.1- to 29.3-fold (16alpha- and 2alpha-TH activities, respectively, lower dose) in males, and up to a 7-fold increase (2beta-TH activity, higher dose) in females was obtained. After repeated treatment, hepatic 6beta-, 16beta-, 2alpha- and 2beta-TH activities were reduced up to approximately 60% in males, whereas no effect was seen in females. In extrahepatic tissues, a generalized increase of different THs was observed. The increase of 6beta-TH activity (CYP3A-linked), one of the most representative isoforms in humans, was sustained in liver and kidney by means of Western immunoblotting, using rabbit polyclonal antibodies anti CYP3A1/2. On the whole, a complex pattern of induction/suppression of CYP-dependent reactions was achieved depending on sex and tissue. The data are consistent with co-toxic, co-carcinogenic and promoting potentials of this fungicide and provide information of interest in evaluating the risk associated with human exposure.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
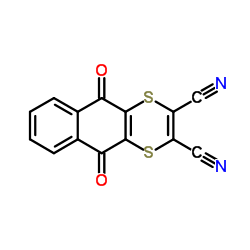 |
Dithianon
CAS:3347-22-6 |
C14H4N2O2S2 |
|
Effect of thiol blocking agents on the binding of T3 and T4 ...
1981-09-01 [Acta Endocrinol. 98(1) , 68-72, (1981)] |
|
Identification of ABC transporter genes of Fusarium graminea...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8 , e79042, (2013)] |
|
In vitro cytotoxic and cell transforming activities exerted ...
1993-01-01 [Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 21(1) , 81-6, (1993)] |
|
Influence of the amendment of corn straw on the degradation ...
2005-01-01 [Environ. Pollut. 133(1) , 63-70, (2005)] |
|
Biomarkers of effect in evaluating dithianon cocarcinogenesi...
1997-02-26 [Cancer Lett. 113(1-2) , 221-8, (1997)] |