Relaxation modulus of denture base resin reinforced with woven glass fibers.
Takahito Kanie, Hiroyuki Arikawa, Koichi Fujii
Index: Dent. Mater. J. 21(1) , 1-8, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This study examined the reinforcing effect of woven glass fibers on the relaxation modulus by three-point loading of denture base resin. Three sandwich-type flexure test specimens polymerized by heating were used, all 3 mm thick: glass fibers in compression (U type); glass fibers in the center (C type); and glass fibers in tension (L type). Unreinforced specimens (ACR) were produced as a control. The relaxation modulus after 8 sec from the start of stress (Er(8)) was calculated from stress relaxation curves. In the glassy state, the Er(8)s of the U and L types were greater than those of the ACR and C types. In the rubbery state (plateau region), the Er(8)s of the U and L types were greater than those of the ACR and C types. The woven glass fibers added to the U and L type specimens increased the relaxation modulus of PMMA near the oral temperature; moreover, they inhibited stress relaxation when the temperature increased.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
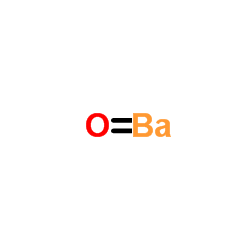 |
Oxobarium
CAS:1304-28-5 |
BaO |
|
Thermal, structural, optical, and dielectric properties of (...
2007-03-01 [J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7(3) , 1006-13, (2007)] |
|
Effects of monomer ratios and highly radiopaque fillers on d...
2009-01-01 [Dent. Mater. 25(11) , 1411-8, (2009)] |
|
Enhancement of ferroelectric polarization stability by inter...
2012-03-02 [Adv. Mater. 24(9) , 1209-16, (2012)] |
|
Oxygen-17 hyperfine structures in the pure rotational spectr...
2007-11-28 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9(44) , 5897-901, (2007)] |
|
The near-infrared broadband emission from bismuth-doped GeO2...
2008-06-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 70(1) , 122-5, (2008)] |