6R-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin is involved in brain vulnerability of senescence-accelerated mouse during the processes of aging.
K Yoshimoto, T Yoshida, A Hirano, S Ueda
Index: Growth. Dev. Aging 61(3-4) , 157-65, (1997)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of age on the dopamine (DA) turnover and 6R-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (6R-BH4), a cofactor for monooxygenases, were investigated in the striatum and midbrain of the senescence accelerated mouse (SAM) at 6, 12 and 15 months old. 6R-BH4 and DA levels were decreased significantly in the striatum of 15-month-old SAM-P/1 (senescence accelerated prone) mice. At 12 months old, DA level was decreased significantly in the striatum of SAM-P/1 compared with SAM-R/1 (senescence accelerated resistant) mice. The reduction of striatal DA level was shown to be related to the depletion of 6R-BH4 in the striatum during the processes of aging. Age-related decreases in striatal dopamine function occurred in SAM-P/1 mice earlier than in the SAM-R/1 mice. The striatal [DOPAC]/[DA] ratio, as the index of DA turnover, was increased significantly in the 15-month-old SAM-P/1 mice. On the other hand, the DA, 6R-BH4 levels and the ratio of [DOPAC]/[DA] did not show any changes in the midbrain of SAM-P/1 and SAM-R/1 during the processes of aging. It was suggested that brain vulnerability with aging may be associated with the levels of 6R-BH4.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
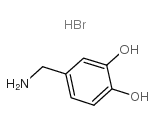 |
3,4-DIHYDROXYBENZYLAMINE HYDROBROMIDE
CAS:16290-26-9 |
C7H10BrNO2 |
|
Simultaneous determination of electroactive and non-electroa...
2010-09-23 [Anal. Chim. Acta 678(1) , 39-43, (2010)] |
|
Selective extraction of catecholamines by packed fiber solid...
2015-01-01 [Biomed. Chromatogr. 29(1) , 103-9, (2014)] |
|
ERK5 induces ankrd1 for catecholamine biosynthesis and homeo...
2016-03-01 [Cell. Signal. 28 , 177-89, (2016)] |
|
Oxidation of 3,4-dihydroxybenzylamine affords 3,4-dihydroxyb...
1995-10-01 [Pigment Cell Res. 8(5) , 250-4, (1995)] |
|
Application of a novel, plastic formed carbon as a precolumn...
1995-12-22 [J. Chromatogr. A. 718(2) , 267-72, (1995)] |