| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
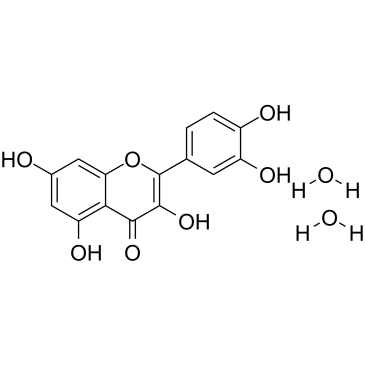 |
Quercetin dihydrate
CAS:6151-25-3 |
|
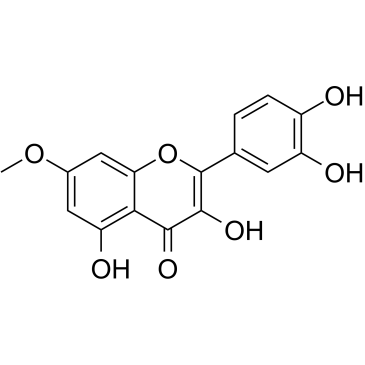 |
beta-Rhamnocitrin
CAS:90-19-7 |
|
 |
Kaempferol
CAS:520-18-3 |
|
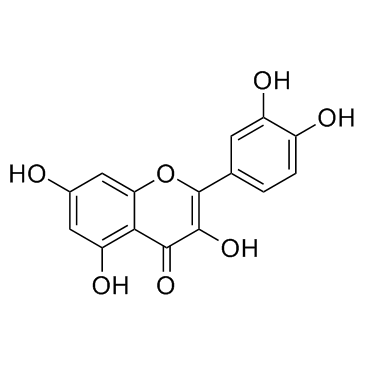 |
Quercetin
CAS:117-39-5 |
|
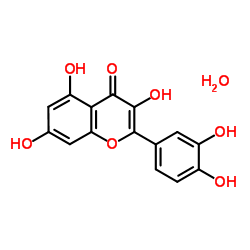 |
Quercetin (hydrate)
CAS:849061-97-8 |