The beta-adrenoceptor agonist clenbuterol is a potent inhibitor of the LPS-induced production of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in vitro and in vivo.
C A Izeboud, M Monshouwer, A S van Miert, R F Witkamp
Index: Inflamm. Res. 48 , 497-502, (1999)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To investigate the suppressive effects of the beta-agonist clenbuterol on the release of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-model of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo.Human U-937 cell line (monocyte-derived macrophages), and male Wistar rats (200-250 g).U-937 macrophages were incubated with LPS at 1 microg/ml, with or without 1.0 mM-0.1 nM test drugs (clenbuterol and other cAMP elevating agents) for 1-24 h. Rats were administered either 1 or 10 microg/kg clenbuterol (or saline) orally, 1 h before intraperitoneal administration of 2 mg/kg LPS.TNF-alpha and IL-6 time-concentration profiles were determined both in culture media and plasma, using ELISA' s and bioassays. LPS-mediated release of both cytokines was significantly suppressed by clenbuterol.The beta-agonist clenbuterol very potently suppresses the LPS-induced release of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 both in vitro and in vivo.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
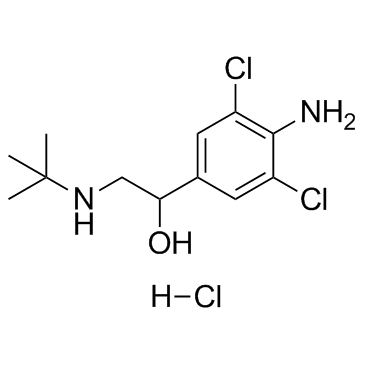 |
Clenbuterol hydrochloride
CAS:21898-19-1 |
C12H19Cl3N2O |
|
Mutagenicity and DNA-damaging potential of clenbuterol and i...
2015-03-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 77 , 82-92, (2015)] |
|
Detection of clenbuterol hydrochloride residuals in pork liv...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0122005, (2015)] |
|
Study of interaction between agonists and asn293 in helix VI...
1999-11-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 56 , 909, (1999)] |
|
Neuroprotection mediated via neurotrophic factors and induct...
[Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 30 , 176-188, (1999)] |
|
Clenbuterol residues in pig muscle after repeat administrati...
2010-11-01 [Meat Science 86 , 733-7, (2010)] |