The molecular species composition of individual diacyl phospholipids in human platelets.
V G Mahadevappa, B J Holub
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 713(1) , 73-9, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The molecular species composition of the individual diacyl phospholipids was determined in human platelets. The 1-acyl (16:0, 18:0, etc.) homologues of the various 2-acyl (16:0, 18:1, 18:2, 20:4, etc) species of the phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol were assessed by the use of thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography in combination with specific lipases for establishing the positional distribution of the fatty acyl chains and generating the diacylglycerol derivatives. A marked heterogeneity was found in the complement of individual molecular species associated with the different platelet phospholipids. The 1-16:0 2-18:1 species predominated in the phosphatidylcholine (21% of total) but contributed only 5%, 2%, and trace amounts to the ethanolamine, inositol, and serine phospholipids, respectively. The 1-stearoyl 2-arachidonoyl species was by far the most prevalent one in the diacyl phosphatidylethanolamine (47% of total) and phosphatidylinositol (71% of total) but represented only 10% of the phosphatidylcholine. The 1-18:0 2-18:1 (37%) plus 1-18:0 2-20:4 (41%) together contributed 78% to the total phosphatidylserine. Interestingly, the 1-stearoyl 2-arachidonyl phosphatidylinositol represented only 6 mol% of the total diacyl phospholipid in human platelets. Of the total mixed 1-acyl 2-20:4 species in human platelets, 31, 35, 17 and 17% was found in the phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylinositol, respectively. These results indicate that the mechanisms involved in the release of arachidonate for prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis would need to possess a profound degree of selectivity if any single molecular species of a given platelet phospholipid were the source of the released arachidonic acid.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
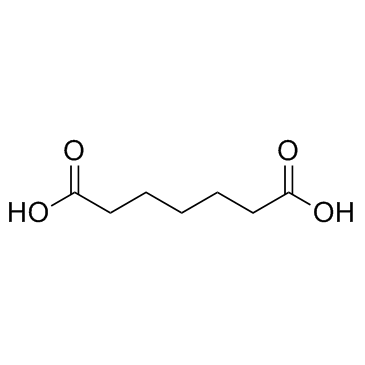 |
Pimelic acid
CAS:111-16-0 |
C7H12O4 |
|
Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a ...
1994-06-01 [Clin. Chem. 40(6) , 862-6, (1994)] |
|
Concentrations of riboflavin and related organic acids in ch...
2000-04-01 [Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71(4) , 978-86, (2000)] |
|
Azelaic acid--biochemistry and metabolism.
1989-01-01 [Acta Derm. Venereol. Suppl. (Stockh.) 143 , 8-13, (1989)] |
|
Pattern of aliphatic dicarboxylic acids in uremic serum incl...
1979-11-15 [Clin. Chim. Acta 99(1) , 71-83, (1979)] |
|
The analysis of thiodiglycollic acid by selected ion monitor...
1986-04-15 [Clin. Chim. Acta 156(1) , 85-90, (1986)] |