Anti-hepatotoxic effects of 3,4-methylenedioxyphenol and N-acetylcysteine in acutely acetaminophen-overdosed mice.
Victor Raj Mohan Chandrasekaran, Se-Ping Chien, Dur-Zong Hsu, Ming-Yie Liu
Index: Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 30(10) , 1609-15, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
3,4-Methylenedioxyphenol (sesamol) is effective against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rats. Whether sesamol's anti-hepatotoxic effect is comparable to that of N-acetylcysteine has never been studied. We investigated the anti-hepatotoxic effects of sesamol and N-acetylcysteine on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Equimolar doses (1 mmol/kg) of sesamol and N-acetylcysteine significantly inhibited acetaminophen (300 mg/kg)-increased serum aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase levels 6 h post-administration. Sesamol and N-acetylcysteine maintained hepatic glutathione levels and inhibited lipid peroxidation. Moreover, the combination of sesamol and N-acetylcysteine antagonistically inhibited sesamol's protection against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. We conclude that the protective effect of sesamol against acetaminophen-induced liver damage is comparable to that of N-acetylcysteine by maintaining glutathione levels and inhibiting lipid peroxidation in mice.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
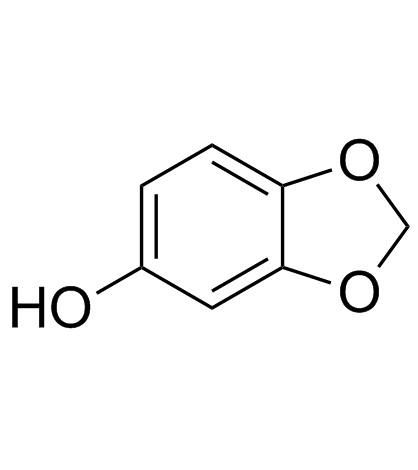 |
Sesamol
CAS:533-31-3 |
C7H6O3 |
|
Synthesis and photopolymerization kinetics of benzophenone s...
2013-02-01 [Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 12(2) , 323-9, (2013)] |
|
Comparison of the simple cyclic voltammetry (CV) and DPPH as...
2012-01-01 [Molecules 17(5) , 5126-38, (2012)] |
|
The interaction of sesamol with DNA and cytotoxicity, apopto...
2013-11-01 [Food Chem. 141(1) , 289-96, (2013)] |
|
A novel role of sesamol in inhibiting NF-κB-mediated signali...
2011-01-01 [J. Biomed. Sci. 18 , 93, (2011)] |
|
A modified sesamol derivative inhibits progression of athero...
2011-03-01 [Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31(3) , 536-42, (2011)] |