| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
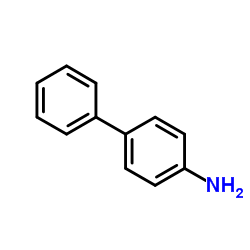 |
4-Aminobiphenyl
CAS:92-67-1 |
|
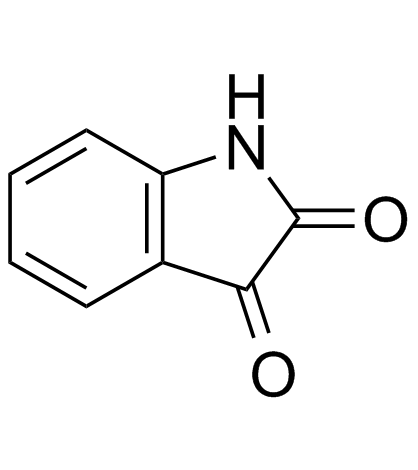 |
isatin
CAS:91-56-5 |
|
 |
4-Phenoxyaniline
CAS:139-59-3 |