| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
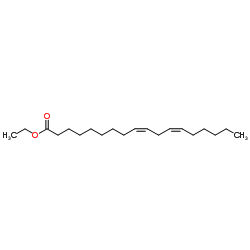 |
Ethyl linoleate (JAN)
CAS:544-35-4 |
|
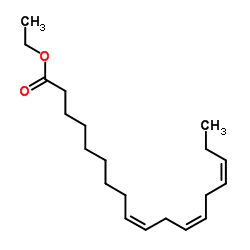 |
Ethyl linolenate
CAS:1191-41-9 |
|
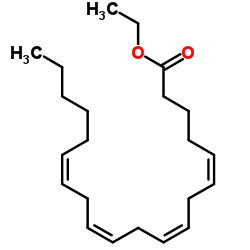 |
Ethyl (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-icosatetraenoate
CAS:1808-26-0 |