| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Ethyl Stearate
CAS:111-61-5 |
|
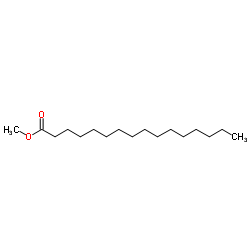 |
Methyl palmitate
CAS:112-39-0 |
|
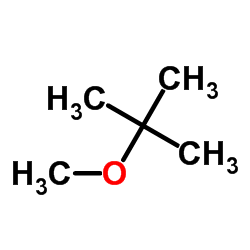 |
Methyl tert-butyl ether
CAS:1634-04-4 |
|
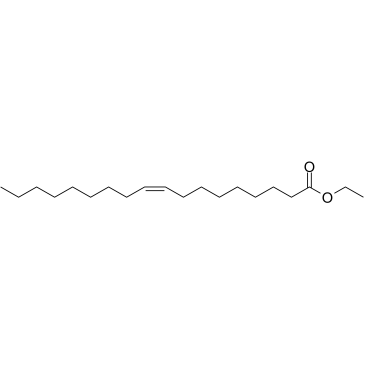 |
Ethyl Oleate
CAS:111-62-6 |
|
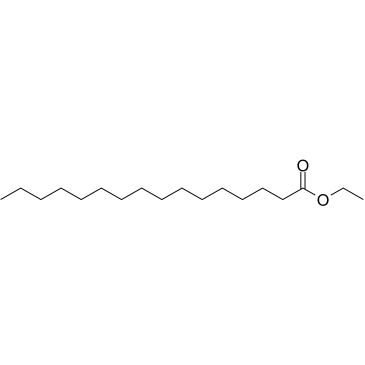 |
Ethyl palmitate
CAS:628-97-7 |
|
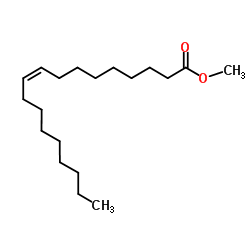 |
Methyl oleate
CAS:112-62-9 |
|
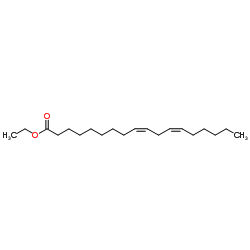 |
Ethyl linoleate (JAN)
CAS:544-35-4 |
|
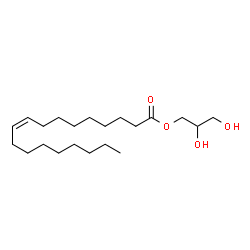 |
Monoolein
CAS:111-03-5 |