| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acrylic acid
CAS:79-10-7 |
|
 |
Guar gum
CAS:9000-30-0 |
|
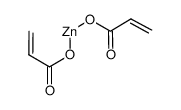 |
Zinc acrylate
CAS:14643-87-9 |