Pyomyositis in children: early diagnosis and treatment.
Gregory I Mitsionis, Gregory N Manoudis, Marios G Lykissas, Ioanna Sionti, Eustathios Motsis, Anastasios D Georgoulis, Alexandros E Berisa
Index: J. Pediatr. Surg. 44(11) , 2173-8, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This study was conducted to evaluate early diagnosis, clinical course, and treatment outcome in children with pyomyositis.Between 2001 and 2006, 6 children with a mean age of 7.2 years were diagnosed and treated for pyomyositis in our clinic. The most common site of involvement was the hip and thigh region. All patients underwent early magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination that played a significant role in the early diagnosis and management of the disease.Staphylococcus aureus was the most common pathogen and was identified in 3 cases. Intravenous antibiotics were administered and were followed by oral agents for an additional period. The duration of therapy ranged from 3 to 6 weeks. No surgical intervention was needed. Magnetic resonance imaging was used to evaluate response to the therapy.Although pyomyositis is a rare disease, it should be considered in the differential diagnosis of immediate onset of musculoskeletal pain in children. Early diagnosis and antibiotic treatment are important as major complications such as abscess formation and sepsis can be avoided. Having a high sensitivity to reactive inflammatory changes, MRI is a valuable tool in the armamentarium of the clinician in early diagnosis of pyomyositis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
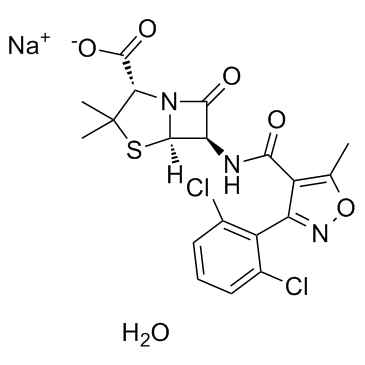 |
Dicloxacillin sodium
CAS:13412-64-1 |
C19H18Cl2N3NaO6S |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the predicti...
2010-07-19 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010)] |
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-indu...
2010-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010)] |
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
2013-01-01 [BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013)] |
|
Intracellular activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus...
2009-05-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 , 1874-83, (2009)] |
|
Do surface active parenteral formulations cause inflammation...
2015-04-30 [Int. J. Pharm. 484(1-2) , 246-51, (2015)] |