Flush induced by fluoroquinolones in canine skin.
M Kurata, Y Kasuga, E Nanba, H Nakamura, T Asano, K Haruta
Index: Inflamm. Res. 44(11) , 461-5, (1995)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The flush induced by two fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents, balofloxacin and ofloxacin, was studied in beagle dogs. Intradermal injection of the fluoroquinolones at concentrations above 10(-5) M produced a localized flushed area. The flush responses to fluoroquinolones were inhibited by co-administration with H2-antagonist(s) (ranitidine or cimetidine), but not with H1-antagonist(s) (mepyramine or chlorpheniramine). Similar inhibitory effects of these H2-antagonists were observed for the response to histamine. The flush responses to fluoroquinolones were inhibited by a local pretreatment with compound 48/80 administered to deplete the local stores of mast cell-bound histamine. When the fluoroquinolones were orally administered at a dose of 400 mg/kg, the concentration of histamine in plasma was increased, being accompanied by systemic erythema. These results indicate that the flush induced by fluoroquinolones is mediated by histamine release from canine cutaneous mast cells and H2-receptor stimulation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
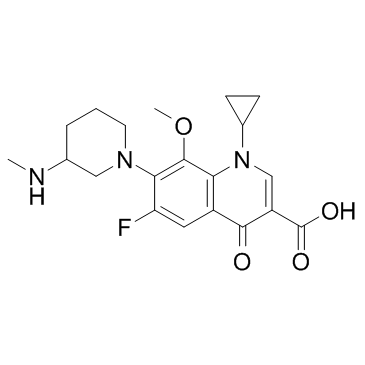 |
Balofloxacin
CAS:127294-70-6 |
C20H24FN3O4 |
|
Determination of the new fluoroquinolone balofloxacin and it...
1995-06-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 45(6) , 716-8, (1995)] |
|
Photoallergenicity of a fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent ...
1998-01-01 [Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 11(4-5) , 232-40, (1998)] |
|
Gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin, and balofloxacin resistance due ...
2009-01-01 [Ophthalmic Res. 42(1) , 43-8, (2009)] |
|
Alterations of protein complexes and pathways in genetic inf...
2012-09-01 [Mol. Biosyst. 8(9) , 2303-11, (2012)] |
|
High performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionizati...
2007-05-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 850(1-2) , 68-73, (2007)] |