| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
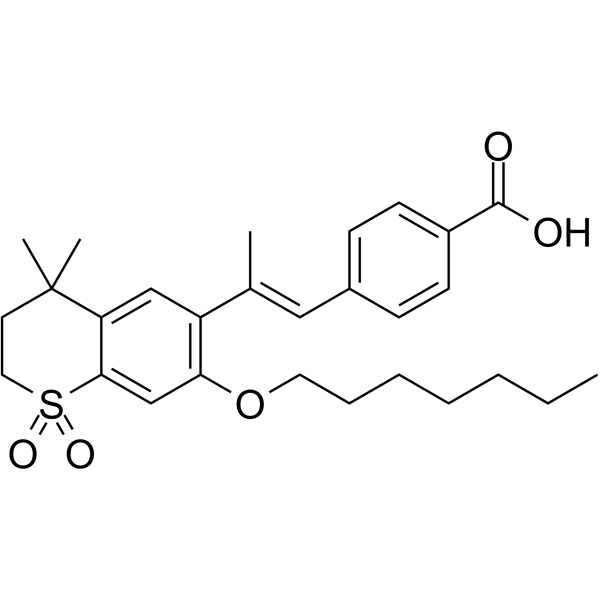 |
Ro 41-5253
CAS:144092-31-9 |
|
 |
AM580
CAS:102121-60-8 |