Factors Influencing the Central Nervous System Distribution of a Novel Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor GSK2126458: Implications for Overcoming Resistance with Combination Therapy for Melanoma Brain Metastases.
Shruthi Vaidhyanathan, Brynna Wilken-Resman, Daniel J Ma, Karen E Parrish, Rajendar K Mittapalli, Brett L Carlson, Jann N Sarkaria, William F Elmquist
Index: J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 356 , 251-9, (2016)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway (Braf/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) have had success in extending survival for patients with metastatic melanoma. Unfortunately, resistance may occur via cross-activation of alternate signaling pathways. One approach to overcome resistance is to simultaneously target the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. Recent reports have shown that GSK2126458 [2,4-difluoro-N-(2-methoxy-5-(4-(pyridazin-4-yl)quinolin-6-yl)pyridin-3-yl) benzenesulfonamide], a dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, can overcome acquired resistance to Braf and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibitors in vitro. These resistance mechanisms may be especially important in melanoma brain metastases because of limited drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. The purpose of this study was to investigate factors that influence the brain distribution of GSK2126458 and to examine the efficacy of GSK2126458 in a novel patient-derived melanoma xenograft (PDX) model. Both in vitro and in vivo studies indicate that GSK2126458 is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp), two dominant active efflux transporters in the blood-brain barrier. The steady-state brain distribution of GSK2126458 was 8-fold higher in the P-gp/Bcrp knockout mice compared with the wild type. We also observed that when simultaneously infused to steady state, GSK212658, dabrafenib, and trametinib, a rational combination to overcome mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor resistance, all had limited brain distribution. Coadministration of elacridar, a P-gp/Bcrp inhibitor, increased the brain distribution of GSK2126458 by approximately 7-fold in wild-type mice. In the PDX model, GSK2126458 showed efficacy in flank tumors but was ineffective in intracranial melanoma. These results show that P-gp and Bcrp are involved in limiting the brain distribution of GSK2126458 and provide a rationale for the lack of efficacy of GSK2126458 in the orthotopic PDX model. Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
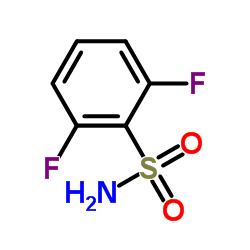 |
2,6-Difluorobenzenesulfonamide
CAS:60230-37-7 |
C6H5F2NO2S |
|
Factors influencing the CNS distribution of a novel MEK-1/2 ...
2014-08-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 42(8) , 1292-300, (2014)] |
|
Thermodynamic parameters for the association of fluorinated ...
2007-01-08 [Chem. Asian J. 2(1) , 94-105, (2007)] |
|
Insect growth regulators. Analogs of TH-6038 and TH-6040. Ol...
[J. Agric. Food Chem. 24(5) , 1065-1068, (1976)] |