| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
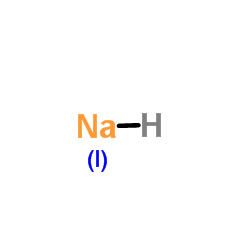 |
α-Lactalbumin
CAS:9051-29-0 |
|
 |
LACTALBUMIN
CAS:9013-90-5 |